PhD programs
Matthieu Delahaye (2023-) "Explainable and unbiased artificial intelligence: towards an understanding and representation of urban security phenomena"
Supervisors: Philippe Lenca, Lina Fahed & Florent Castagnino
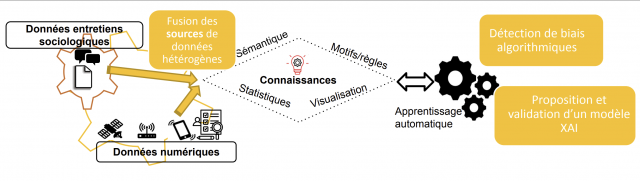
Recently, the deployment of AI models, often qualified as black boxes, in sensitive sectors such as urban security has raised the need for explanation for all the actors involved in the decision support process of these models. This PhD project is part of the initiative to improve the reflexivity that urban security actors can have on their own practice by improving their understanding of the evolution of urban security phenomena. The main objective of the research here lies in (i) detecting and correcting the biases that may arise throughout the development process of the AI model, (ii) proposing a machine learning model for detecting and predicting the evolution of these phenomena. This model needs to be interpretable and explainable using different explanation formats adapted to the context and background knowledge of the decision-maker.
Yann Jourdin (2023-) "Group decision-making: modeling, learning and interpretability"
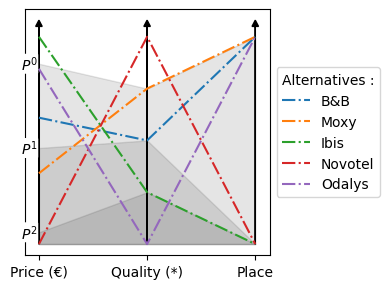
Multi-criteria decision support aims to help a decision-maker make better-informed decisions through the use of preference models. The aim of this thesis is to adapt a preference model using reference profiles (RMP) to the case where a group of decision-makers has to find a compromise. To this end, the problem is divided into three stages: the first concerns the creation of a variant of the RMP model that takes into account the complexity of interactions between decision-makers; the second focuses on the learning of this model from the decision-makers' preferences; and the last concerns the automatic generation of an interpretation of the model's final recommendation.
Joseph Thompson (2023-) "Integrating machine learning methods into meta-heuristics: an algorithm selection-cooperation system for solving combinatorial optimization problems"
Matthieu Bachelot (2022-) "Temporal and heterogeneous data mining for modeling and detecting misleading information"

The main objective of this research project is to identify recurring patterns related to the spread of false information. Our unique approach is based on French data, by combining different sources of information, namely online press articles and Twitter posts. The first part of the thesis focuses on the creation and validation of this dataset by conducting exhaustive statistical analyses, and comparing these results with those of the Anglo-Saxon literature. This will allow us to provide the decisive elements for Fake News detection via machine learning methods on graphs. This will make it possible to work on early detection, or even the modeling of "generic" misleading information propagation.
Owein Thuillier (2022-) " Artificial intelligence for configuring multistatic sonar arrays"

Bachtiar Herdianto (2022-) "Machine learning And Matheuristics algorithms for Urban Transportation"
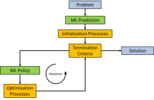
Dubon Rodrigue (2022-) "Simplifying energy network architecture by aggregating AI-based nodes"
The district heating network (DHN) facilitates the integration of renewable heat producers and enables efficient energy transport with an optimal control. To take advantage of these advantages, it is necessary to optimize and simulate the network, which is computationally expensive. Dubon joined the Lab-STICC DECIDE team in October 2022 and is also affiliated to the GEPEA OSE team. From the formulation of the DHN as a connected graph, in his thesis, Dubon studies a new method to reduce this simulation cost by aggregating similar consumer nodes using the latest artificial intelligence architectures. His objective is to develop two complementary models: an unsupervised model to identify similar consumer nodes and a time-dependent supervised model to learn the physical dynamics of these consumer nodes.
Erwan Alincourt (2022-) "Mapping, anomaly detection and reaction to detection on Industrial Systems: application to military and civil ships"
Supervisors : Yvon Kermarrec, Philippe Lenca, CC Xavier.
Modern boats are much more efficient than their 19th or 20th century ancestors. As with factories, these improvements have been made possible by the extensive automation of systems. These systems, which are hybrids of computer and mechanical systems, are known as cyber-physical systems. PLCs (ICS / SCADA) that control machines and navigation systems such as AIS are just a few examples of these CPS. Like all computer systems, they are vulnerable to cyber attacks, but a malfunction on these systems can lead to disaster in the real world. Moreover, it is very difficult to modify these systems to make them "cyber by design". That's why it's so important to be able to detect the occurrence of a cyber attack on these systems at an early stage. There are several ways of doing this, including signature databases, expert rules and AI. The research questions identified at this stage are as follows: What role can AI play in detecting attacks on physical cyber systems on ships? How can we evaluate the performance of a cyber attack detection algorithm in a maritime CPS context? How can the decision-maker choose the most efficient algorithm or combination of algorithms in this context?
Julien Mercier (2020-2024) "Benefits and limits of geolocalized augmented reality for learning about biodiversity"
Supervisors: Erwan Bocher, Olivier Ertz

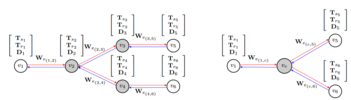
Antoine Mallégol (2020-2023) "Multi-objective optimization of coupled energy systems"
The objective of Antoine Mallégol's thesis work is to propose an optimization method for a coupled energy system, composed of an electrical network and a heat network that can interact with each other. The main challenge of this work is to solve a complex model with a long time horizon. Different modeling and optimization methods are proposed: mixed integer linear programming, heuristics, and metaheuristics. A multi-objective approach allows to improve the costs and the environmental impact of the system.
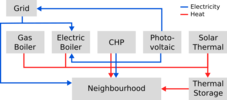
Fred Gonsalves (2020-2023) "Data mining and decision support for short-term monitoring and forecasting of a cruise ship's energy efficiency"
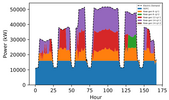
Incorporated into the DECIDE team at LabSTICC since 2020 and the ECORIZON team at Chantiers de l'Atlantique since 2019, Fred is conducting a thesis focused on reducing energy consumption and the environmental footprint of cruise ships. The scientific challenges of his work include integrating data from various sources (sensors, weather archives, supplier data, etc.), applying machine learning techniques, modeling the systems and subsystems that make up the ship, and developing decision-support tools, from design to operation. His work is carried out under a CIFRE thesis, in partnership with IMT Atlantique and Chantiers de l'Atlantique.
Quentin Perrachon (2020-) "Intelligent scheduling for the industry of the future"
Quentin Perrachon is an industrial PhD student as part of a collaboration between the DECIDE team at Lab-STICC at the University of South Brittany and the company Herakles based in Vannes. Herakles develops and distributes an ERP software and wishes to offer an additional tool to provide solutions to scheduling problems for small to medium-sized manufacturing workshops. A generic modeling approach is proposed to solve problems for a wide variety of industries, this modeling is based on the flexible job shop scheduling problem with the addition of several industrial constraints, such as resource unavailability or the potentially partial necessity of resources for certain operations. The goal is to maintain just one model and tool capable of meeting the demands of different industries. Originating from operations research, exact and metaheuristic approaches based on neighborhood techniques are explored and proposed to solve this problem.
Hadi M. Y. Khalilia (2019-) “Generating Diversity-Aware Multilingual Lexical-Semantic Resources”
Languages are known to describe the world in diverse ways. While linguists have for long studied phenomena related to lexical diversity, such results are almost never used in computational applications. The goal of the PhD thesis is to explore phenomena of lexical diversity across languages and to propose methodologies for a systematic, large-scale creation of diversity-related computational language resources. The methodologies are of a hybrid nature, involving the reuse of existing results from linguistics, automated algorithms, as well as contributions from native speakers. For this reason, while the thesis is mainly situated in the field of computer science, it is interdisciplinary with elements from linguistics, citizen science, and artificial intelligence.
Kobina Piriziwè (2019-2022) "New 3D collaborative graph visualizations for intra and inter communities'relationships exploration"
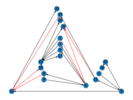
The aim of this thesis was to study the contributions of immersive 3D visualization compared to classical 2D visualization in order to improve the exploration and analysis of intra-community and inter-community relationships represented as graphs. After an analysis of the state of the art on graph theory and its applications to social network analysis and on graph visualization methods, we proposed two graph visualization approaches: an exocentric visualization, which allows a user to manipulate a graph as an object, to intuitively visualize the centrality of the nodes and an egocentric visualization, especially adapted to the exploration of a graph in an immersive environment, where our mechanism of retraction of the graph display space allows a user to have an overall view of the graph while remaining in egocentric mode. The applications of this work are both civilian and military..
Mohadese Basirati (2019-2022) "Zoning management in marine spatial planning : multi-objective optimization and agent-based conflict resolution"
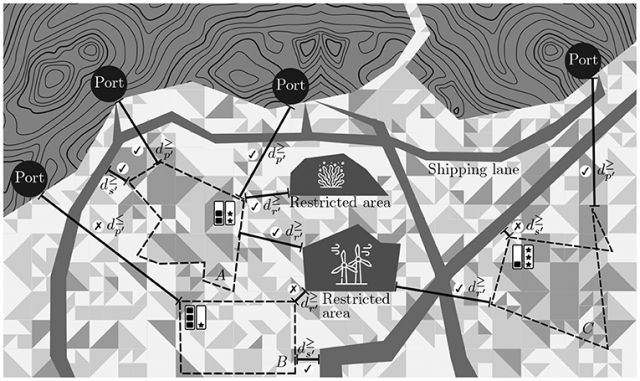
The challenge of this thesis is to develop a spatial decision support system to locate and allocate areas of marine space to multiple stakeholders, despite potentially conflicting initial objectives and constraints. To answer this question, in this thesis we focus on three different requirements as follows: 1) Model the problem in a realistic GIS framework and formulate a mathematical model to solve it, 2) Be able to propose solutions for large-scale problems, 3) Develop a decision-making process that helps multiple stakeholders resolve possible conflicts by reaching a compromise. In line with these objectives, this thesis proposes a multi-objective multi-agent system (MOMAS) that simulates the multi-level decision-making processes involved in managing the spatial zoning of marine uses, with three main contributions: 1) Multi-objective integer linear programming (MOILP), 2) Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MOEA), 3) Cooperative decision processes with multi-agent systems (MAS) and heuristic methods. This thesis proposes a formal and executable approach to address the problem of space zoning management with multiple objectives and actors. In the event of conflict, different cooperation scenarios are compared and ranked. Experimental results on synthetic datasets highlight the fact that good compromises can be reached when actors agree to cooperate. The proposed work paves the way for future on-line decision support tools applied to real cases.
Maryam Karimi-Mamaghan (2019-2022) "Hybridizing metaheuristics with machine learning for combinatorial optimization : a taxonomy and learning to select operators"
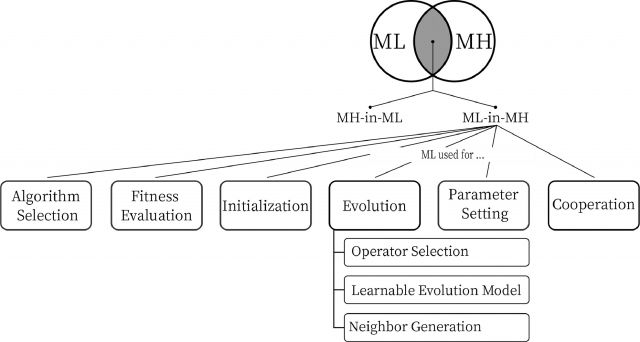
This thesis integrates machine learning techniques into meta-heuristics to solve combinatorial optimization problems. This integration will guide meta-heuristics towards making better decisions and consequently making meta-heuristics more efficient. This thesis, first of all, provides a comprehensive but technical review of the literature and proposes a unified taxonomy on the different ways of integration. For each type of integration, a full analysis and discussion is provided of the technical details, including challenges, advantages, disadvantages and prospects. We then focus on a particular integration and address the problem of adaptive operator selection in meta-heuristics using reinforcement learning techniques. More specifically, we propose a general framework that integrates the Q-learning algorithm into the iterated local search algorithm in order to adaptively select the most appropriate search operators at each stage of the search process based on their performance history. The proposed framework is applied to two combinatorial optimization problems, the traveling salesman problem and the permutation flowshop scheduling problem. In both applications, the proposed framework performs better in terms of solution quality and convergence rate than a random selection of operators. Furthermore, we observe that the proposed framework shows state-of-the-art behavior when solving the permutation flowshop scheduling problem.
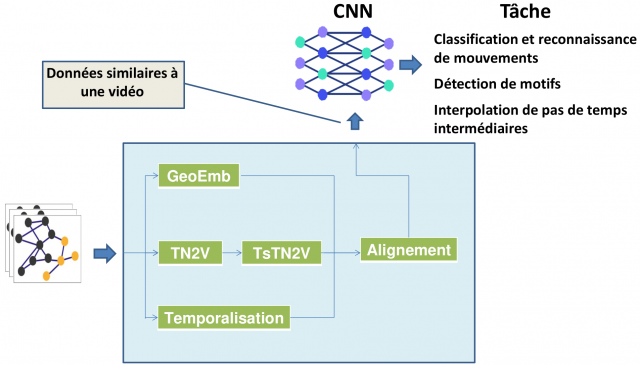
Mounir Haddad (2018-2022) "Embedding temporal graphs: temporalization of static methods and alignment".